Svelte1
- 9
- 2
- Homework Statement
- Need to set the derivative of m(x) to 0.
- Relevant Equations
- taking moments..
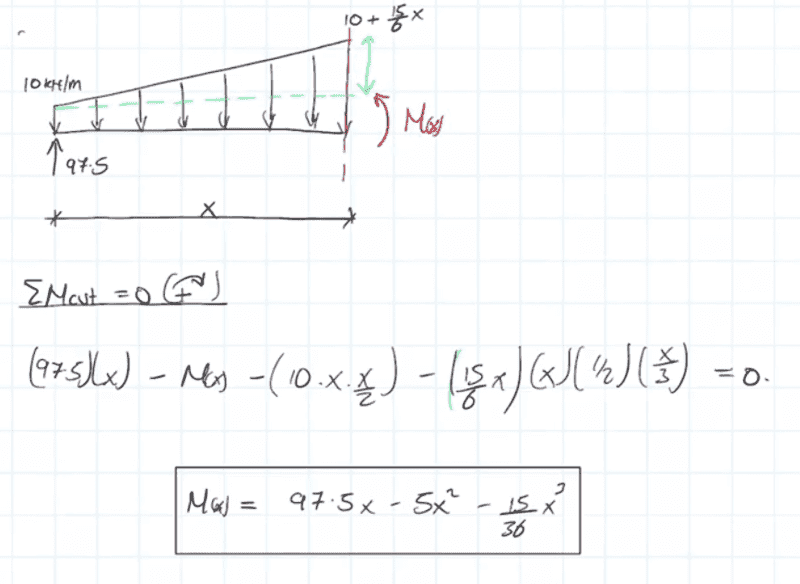
Every time I have taken moments before I have been able to solve for the required unknown regardless of what point I choose, unless there is more than 1 unknown! However I tried taking moments from the far left point load of 97.5 this time and I get the wrong answer. I don't understand why? Thankyou! This image details the correct answer taking the moment from the hypothetical cut so as to find the internal moment values.
Last edited: