SUMMARY
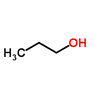
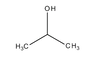
The boiling point of 2-propanol is lower than that of 1-propanol due to the molecular structure and the arrangement of intermolecular forces. 1-propanol, with its hydroxyl group positioned at the end of the molecule, exhibits stronger hydrogen bonding and greater dispersion forces compared to 2-propanol, where the hydroxyl group is centrally located. This results in a higher density of hydrogen bonds in 1-propanol, requiring more energy to break these interactions, thus leading to a higher boiling point. The hierarchy of intermolecular forces—hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and dispersion forces—plays a crucial role in this phenomenon.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of molecular geometry and its impact on intermolecular forces
- Knowledge of hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and dispersion forces
- Familiarity with the properties of alcohols, specifically 1-propanol and 2-propanol
- Basic concepts of boiling point determination and kinetic energy
NEXT STEPS
- Study the molecular structure of alcohols and their impact on physical properties
- Explore the differences in intermolecular forces among various alcohols
- Learn about the boiling point trends in organic compounds based on molecular interactions
- Investigate the role of molecular geometry in determining physical properties of substances
USEFUL FOR
Chemistry students, educators, and professionals interested in organic chemistry, particularly those studying the properties of alcohols and intermolecular forces.