lemd
- 31
- 0
Hi,
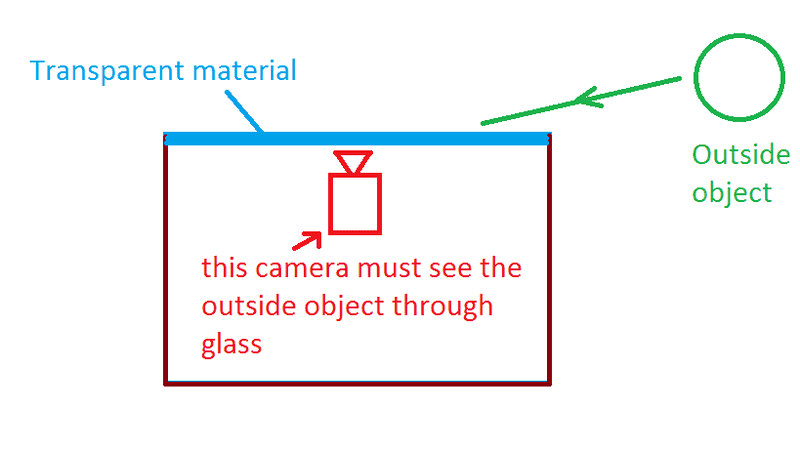
I am designing a device which has cameras need to see through a sheet of glass at angle very low, near zero. And at that angle most of light is reflected so it is very hard to see.
- The surface of the transparent material must be flat and smooth
- The camera must see outside object at angle smaller than 5 degree
- Optical devices could be arranged below the transparent surface, e.g mirror, prism, but the main problem is that most light is reflected and doesn't go inside
I wonder is there any solution for this? I.e some kind of coating to let light go through at low angle? Any help would be appreciate
Please refer to image below:
Regards
I am designing a device which has cameras need to see through a sheet of glass at angle very low, near zero. And at that angle most of light is reflected so it is very hard to see.
- The surface of the transparent material must be flat and smooth
- The camera must see outside object at angle smaller than 5 degree
- Optical devices could be arranged below the transparent surface, e.g mirror, prism, but the main problem is that most light is reflected and doesn't go inside
I wonder is there any solution for this? I.e some kind of coating to let light go through at low angle? Any help would be appreciate
Please refer to image below:
Regards