- #1
Shadowz
- 43
- 0
Hi everyone,
Recently I am working with a research which involves some semiconductors. In the basic level, semiconductor can be classified as intrinsic (undoped) and extrinsic (doped) semiconductor. Then extrinsic semiconductor can be divided into n-type and p-type. For example, the below figure illustrates the n-type semiconductor.
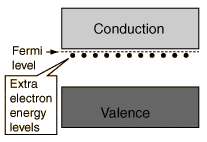
According to my understanding, since semiconductors have large band-gap (not as large as insulator) so that electrons cannot move easily from valence band to conduction band, and that's why people add an additional element to the semiconductor to make them become extrinsic semiconductor. Thus, I expected the extra electrons (for n-type) will move from the extra energy level (as seen in the above figure) to the conduction band and the valence band will not involve in this excitation.
However, as I read more and more about semiconductor and electrochemistry, a lot of authors draw n-type and p-type semiconductors in which electrons move from valence band to conduction band
This is a figure I got from wiki
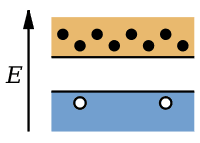
Even though this picture is not great, it represents the idea that for extrinsic semiconductor, electrons move from valence band to conduction band (but if it's true then why they have to add impurities to the intrinsic semicondutor).
Any explanations or suggestions would be great helps for me.
Thanks.
Recently I am working with a research which involves some semiconductors. In the basic level, semiconductor can be classified as intrinsic (undoped) and extrinsic (doped) semiconductor. Then extrinsic semiconductor can be divided into n-type and p-type. For example, the below figure illustrates the n-type semiconductor.
According to my understanding, since semiconductors have large band-gap (not as large as insulator) so that electrons cannot move easily from valence band to conduction band, and that's why people add an additional element to the semiconductor to make them become extrinsic semiconductor. Thus, I expected the extra electrons (for n-type) will move from the extra energy level (as seen in the above figure) to the conduction band and the valence band will not involve in this excitation.
However, as I read more and more about semiconductor and electrochemistry, a lot of authors draw n-type and p-type semiconductors in which electrons move from valence band to conduction band
This is a figure I got from wiki
Even though this picture is not great, it represents the idea that for extrinsic semiconductor, electrons move from valence band to conduction band (but if it's true then why they have to add impurities to the intrinsic semicondutor).
Any explanations or suggestions would be great helps for me.
Thanks.