- #1
anomalocaris
- 23
- 0
Homework Statement
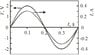
Hello all! Basically, my professor used this graph in our lecture, but I do not really understand how to read it. The graph has three variables, so I'm guessing it is Voltage vs. Current as time increases? One question he asked was "The figure shows the voltage and current for a device. The frequency of the voltage is___" with the correct answer being 2.5 Hz.
Homework Equations
This graph makes very little sense to me, but I know that ω=2∏f
Would the self-inductance formula work here? ε=-L(ΔI/Δt)
This is the only equation I can think of that includes Volts, Amperes, and seconds.
The Attempt at a Solution
I know the sine waves are in phase with different amplitudes, but the arrows pointing in opposite directions must mean something? Should I choose the point where both the emf and the current are zero?
Attachments
Last edited: