- #1
Drazick
- 10
- 2
Homework Statement
The Identity to prove:
Homework Equations
Using Integration by parts
The Attempt at a Solution
I couldn't produce the denominator.
Drazick said:Homework Statement
The Identity to prove:
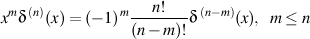
Homework Equations
Using Integration by parts
The Attempt at a Solution
I couldn't produce the denominator.
The Dirac Delta function, denoted as δ(x), is a mathematical concept used in the field of distributions. It is defined as a function that is zero everywhere except at the origin, where it is infinite. It is often referred to as a "point mass" or "impulse" function.
The Dirac Delta function is used to represent certain mathematical objects, such as the Heaviside step function and the Kronecker delta, in terms of distributions. This allows for the manipulation and simplification of equations, making it a useful tool in proving identities.
No, the Dirac Delta function cannot be graphed in the traditional sense because it is a distribution rather than a regular function. However, it can be represented graphically as a spike or impulse at the origin with an area of 1.
The Dirac Delta function is often referred to as a "point mass" because it behaves similarly to a physical point mass in the sense that it has a mass of 1 concentrated at a single point (the origin). This allows for the use of concepts from physics, such as moments and center of mass, in the study of distributions.
The Dirac Delta function has various applications in physics, engineering, and signal processing. It is used to model point sources of energy or mass, such as electric charges or particles, in physical systems. It is also used in solving differential equations and analyzing signals, such as in Fourier transforms.