You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Redshift: Definition and 384 Discussions
In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in frequency and energy, is known as a negative redshift, or blueshift. The terms derive from the colours red and blue which form the extremes of the visible light spectrum.
In astronomy and cosmology, the three main causes of electromagnetic redshift are
The radiation travels between objects which are moving apart ("relativistic" redshift, an example of the relativistic Doppler effect)
The radiation travels towards an object in a weaker gravitational potential, i.e. towards an object in less strongly curved (flatter) spacetime (gravitational redshift)
The radiation travels through expanding space (cosmological redshift). The observation that all sufficiently distant light sources show redshift corresponding to their distance from Earth is known as Hubble's law.Relativistic, gravitational, and cosmological redshifts can be understood under the umbrella of frame transformation laws. Gravitational waves, which also travel at the speed of light, are subject to the same redshift phenomena.
Examples of strong redshifting are a gamma ray perceived as an X-ray, or initially visible light perceived as radio waves. Subtler redshifts are seen in the spectroscopic observations of astronomical objects, and are used in terrestrial technologies such as Doppler radar and radar guns.
Other physical processes exist that can lead to a shift in the frequency of electromagnetic radiation, including scattering and optical effects; however, the resulting changes are distinguishable from (astronomical) redshift and are not generally referred to as such (see section on physical optics and radiative transfer).
The value of a redshift is often denoted by the letter z, corresponding to the fractional change in wavelength (positive for redshifts, negative for blueshifts), and by the wavelength ratio 1 + z (which is >1 for redshifts, <1 for blueshifts).
View More On Wikipedia.org
In astronomy and cosmology, the three main causes of electromagnetic redshift are
The radiation travels between objects which are moving apart ("relativistic" redshift, an example of the relativistic Doppler effect)
The radiation travels towards an object in a weaker gravitational potential, i.e. towards an object in less strongly curved (flatter) spacetime (gravitational redshift)
The radiation travels through expanding space (cosmological redshift). The observation that all sufficiently distant light sources show redshift corresponding to their distance from Earth is known as Hubble's law.Relativistic, gravitational, and cosmological redshifts can be understood under the umbrella of frame transformation laws. Gravitational waves, which also travel at the speed of light, are subject to the same redshift phenomena.
Examples of strong redshifting are a gamma ray perceived as an X-ray, or initially visible light perceived as radio waves. Subtler redshifts are seen in the spectroscopic observations of astronomical objects, and are used in terrestrial technologies such as Doppler radar and radar guns.
Other physical processes exist that can lead to a shift in the frequency of electromagnetic radiation, including scattering and optical effects; however, the resulting changes are distinguishable from (astronomical) redshift and are not generally referred to as such (see section on physical optics and radiative transfer).
The value of a redshift is often denoted by the letter z, corresponding to the fractional change in wavelength (positive for redshifts, negative for blueshifts), and by the wavelength ratio 1 + z (which is >1 for redshifts, <1 for blueshifts).
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
T
I Why does the expanding universe redshift light?
How does the expansion of space cause light to lose energy?- tovisonnenberg
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B How do we know that the universe is still expanding
This idea has always bugged me: If we are looking at the past when observing the redshift of far away galaxies (ex: 10 billions light years).. then how can we tell that the universe at the present time is still expanding at same rate, deaccelerated, or stopped expanding? -

I Redshift and the Friedmann metric
My discussion of the Friedmann metric comes from the derivation presented in section 4.2.1 of the reference: https://www1.maths.leeds.ac.uk/~serguei/teaching/cosmology.pdf I have a couple of simple questions on the derivation. The are placed at points during the derivation.I note the...- redtree
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

I Curve fitting the luminosity distance and redshift data
Can anyone recommend papers that directly curve-fit redshift as a function of luminosity distance for type Ia supernova and gamma ray bursts? I am looking for papers that do not curve-fit the data via an assumed model, even one as simple as Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker (FLRW) metric. I... -
T
B Gravitational Redshift: Will Two Lasers Operate Differently?
If we run two identical lasers and put one at sea level and one on top of a high mountain, will they operate at different frequencies?- Torog
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Cosmological Redshift and Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Has anyone conjectured that the redshift associated with Hubble's constant can be explained by Heisenberg's uncertainty principle? Another words, the further in space away from us a photon is emitted from a galaxy, the longer in time it takes for the photon to reach us. Since the photon has a... -

I Andromeda and the cosmological redshift
I understand that andromeda is blue shifted because it is moving towards us, but do we see any kind of redshift because of the expansion of the universe. Is andromeda less blue shifted than it should be because of cosmological redshift?- nmsurobert
- Thread
- Replies: 28
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Is there a specific unit used to measure redshift?
i have been learning about using redshift to measure the distance of far-flung objects, but in all my research i never saw a specific unit used to quantify how redshifted an object is. to me it seems like an oversight, because such a unit would be very useful for the study of distant galaxies... -
R
I Why are non-relativistic particles not redshifted?
Hey! I was reading some script and when it comes to the cosmological redshift, it says, that only relativistic particles are affected by cosmological redshift. This does feel quite natural, however, I haven't been able to come up with an explanation that shows it with proper physics and... -

B What is the highest redshift (Z number) a galaxy can have?
Galaxies seem to being found further and further back to the BB, At what epoch is it going to be impossible for galaxies to form? https://arxiv.org/abs/0912.4263 -

Insights Coordinate Dependent Statements in an Expanding Universe - Comments
Greg Bernhardt submitted a new PF Insights post Coordinate Dependent Statements in an Expanding Universe Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post. -
E
I Cosmological Redshift: Distinguishing From Doppler Effect
In studying the chapters on cosmology in Misner/Thorne/Wheeler (what a textbook!), I see that the cosmological redshift is different than Doppler. If I understand correctly, it is due to the expansion of the (Friedman, FLRW) universe during the photon’s long journey to us, rather than being due... -

I What Does Redshift and Scale Factor Tell Us About the Size of the Universe?
We can define the relationship between ##z## and ##a(t_e)## as, $$1+z=\frac {a(t_0)=1} {a(t_e)}$$ When we assume ##z=2##, it means that ##a(t_e)=\frac {1} {3}## Is this means that universe was ##\frac {1} {3}## times smaller then now ? If its the case then let's suppose ##z=6## which means...- Arman777
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Redshift Scale Scale factor
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
M
I Atomic Oscillations & Redshift in Sun and Earth
My question is very simple (and I assume it has been discussed before but I cant't find the topic): An atom in the Sun emits a photon detected by an observer on Earth. Disregarding uncertainties and experimental problems relating to the movement of the atom (or assuming we could correct for...- Mickey1
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Is high redshift data a problem for ΛCDM?
A couple of papers in the last couple of years identify problems with the ΛCDM "standard model of cosmology" based upon high redshift astronomy observations. Have there been adequate responses to these concerns? Charles L. Steinhardt, et al., "The Impossibly Early Galaxy Problem" (June 3...- ohwilleke
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Data Phenomenology Redshift
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Cosmology
-

I Best way to filter NED redshift data
i'm using http://ned.ipac.caltech.edu/ui/?q=byparams to extract redshift data. while I'm very happy there is now lots of data available, data requests need to be limited in size or you get an error. i would like to examine the patterns of redshift vs longitude, but that is too much data, i...- nearc
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
G
I How does flux density scale with redshift?
I'm not sure I understand how to correctly scale flux density with redshift. That is, if I observe say 10 Jy at my observing frequency coming from a source at z = 0.3, how can I estimate the flux density I would expect from the same source at z=2? From what I understand, the final scaling is... -
S
I The error bars of redshift drift
Dear all, I am reading the paper "Cosmic dynamics in the era of Extremely Large Telescopes " by Liske et al. about redshift. I get the physical meaning of redshift drift, but when it comes to the error bars, I am confused. - Aren't the error bars given in equation (15) ? - Isn't this function...- shadishacker
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Cosmology
-

I New possible explanation for Hubble redshift
I just saw this news article on the home page of the university I'm working in: http://www.aalto.fi/en/current/news/2017-06-30/ It seems to be about a study that can potentially explain the redshift of distant stars with a mechanism that's related to the interaction of photons with the... -
S
I Systematic Redshift: Exploring Mg II Uses
Hi everyone, I am new to observations and observational terms! I am reading the paper "constraining the time variation of the fine-structure constant" by Srianand et. al in the section "constraining alpha with QSO absorption lines" there is a sentence saying "... rest wavelengths of MG II ...- shadishacker
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Cosmology
-
I Comoving distance and redshift relationship derivation
Hello PhysicsForum, There is something I don't get at the end of this course notes PDF file. In the last section, titled "Comoving distance and redshift", which I have copied below, we have a short derivation of the comoving distance and redshift relation. Almost all is well, the only thing... -

B Conservation of Energy and Expansion Redshift
Since the universe is expanding, photons emitted by distant stars are red-shifted, having their wavelengths stretched out. But, since the energy of a photon is dependent on the inverse of its wavelength, doesn't that mean that the expansion of the universe is causing photons to lose energy? How...- John Morrell
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Cosmology
-

Cosmological Redshift distance to where it begins?
what is thought to be the closest star whose light visible to us now is/has cosmological redshift? perhaps the same answer but in case not: at what LY distance does the prevalent cosmological redshift of distant starlight begin? TY, r- rmpearlman
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
G
B Cosmological Redshift: Where Has the Energy Gone?
As the Universe expands and the photons stretch to longer wavelengths (say from UV photons to the CMBR now) where has the energy gone since longer wavelength photons have less energy? Regards, G.- Glenn G
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Why does expansion redshift light if....
isn't expansion essentially making more space rather than moveing us in it? So why does it redshif light? Or is that just a super facile explanation of expansion that they explain people like me who wouldn't get it?...- unwillingly ignorant
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Cosmology
-
A
B Redshift of distant galaxies....
...does it not simply indicate that the galaxies WERE receding faster IN THE PAST?- Alistair Bingham
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Cosmology
-
R
I How to solve for the volume of the universe / redshift
Hey ! i am having this question to be answered , i am new to the cosmology studies and still a bit confused about some formulas. the question is: (a) The greatest redshift known corresponds to the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CBR) at redshift z 1100 (although the redshift is obtained... -

I Gravitational Redshift: Derivation from Static Metric
I am trying to find a derivation of gravitational redshift from a static metric that does not depend on the equivalence principle and is not a heuristic Newtonian derivation. Any suggestions?- redtree
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
Solving Redshift Confusion Homework Problem
Homework Statement I encountred a question that says : Assume that gravitational interactions between galaxies in groups lead to random galaxy velocities of 300 km/s At what distance would the redshift predicted by Hubble's law dominate over that produced by individual velocities? and what is...- MoAli
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
S
Plotting Density Parameters as a Function of Redshift
I'm trying to plot the density parameters against redshift in Python, so I suppose this is kind of a cross over of programming and physics. I've been given the following two equations in order to do so $$r(z) = \lambda_H \int_{0}^{z} \frac{dz'}{E(z')}$$ $$E(z) = \frac{H(z)}{H_0} = \sqrt...- slothwayne
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

A Redshift data on stars the same distance from earth
Can anyone in the cosmology community direct me to hard research data that specifically demonstrates: there is no detectable redshift difference in stars that are the same distance from the Earth but in all different directions. This is of course related to 'does the universe have a preferred... -
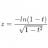
I Why does this redshift v. light travel time equation work?
Why does this redshift versus lighttravel time equation work? z=-ln(1-t)/sqrt(1-t^2) where (z) is the cosmological redshift, and (t) is the look-back time where the present equals 0 and the origin of time equals 1. Ned Wright's cosmology calculator with the default inputs [H_o=69.6... -

A Gravitational Redshift in Newtonian Equivalence Principle?
So I was reading that the equivalence principle of Newton doesn't work because of a thought experiment. They said that an experimenter shoots bullets( 1 per second) from the bottom of the elevator to the top. This happens in outerspace where the elevator moves up with accleration g. And this...- FallenApple
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
P
I Scale factor/redshift formula wrong at the end?
In this video: The professor at the end (at about 7:28), used the formula for scale factor and redshift as a(t) = 1/z, instead of the actual one a(t) = 1/1+z. And when we apply both of them, they give very different results. So, how could the professor use the first formula, which we were...- Phys12
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
P
I How can we measure a galaxy's velocity via a star?
In this video (), we first took the spectrum of a star and then of a galaxy which look like the following: However, what I don't get is: if we take the spectrum of a star and then of the galaxy the star is in, shouldn't it give me the same spectrum as they're moving in the same speed? And if... -
P
I How Can We Measure Redshift Using the Spectrum of a Star?
As far as I know, when we use the spectrum of a star, we see where the absorption lines are and using this, we can detect the elements that are present in the star. We also measure whether those absorption lines are supposed to be for a particular element. But why is it not possible that the... -
J
I Proportionality of the Redshift
Good day all, Sorry if this has been posted a lot before but I've been fiddling with the formulas for the redshift and I came up with a question regarding the proportionality of it. I'm new at this so please bear with me. For the sake of argument, I'm talking about redshift in an expansion with...- JohnnyGui
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Proportionality Redshift
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Is There a Limit to How Much Light Can Be Stretched Out in a Black Hole?
The expansion of our universe stretches out light causing the phenomenon known as "redshift." When light falls into a black hole... Its wavelength gets stretched out infinitely? Light with a flat wavelength? Or is there some limit to how much a wave of light can be stretched out... There's a...- Borrah Campbell
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Redshift
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Why is the redshift not the result of something else
A high GHz mobile signal needs to be close to your house for you to get a good signal without the mast frying nearby residents with too many watts. A LW radio signal on the other hand can be transmitted from a far away country with a less watts. This is because shorter wave lengths are absorbed... -

I What does cosmological redshift do to light
I understand it's definition but i am unsure how it affects light. Does it slow light down? (is this even possible?) Does it stretch light's wavelength? Does it convert light into infrared? Does it make light brighter or dimmer? hmm. thank you for your kind help!- whatphysics
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Could redshift be caused by time speeding up?
This has been bothering me for ages so I'm posting here in the hope someone can answer. If the universe was not expanding and if time was not constant but instead was speeding up why would this not fully account for observed cosmological redshift? Wavelengths of light released long ago would...- paulharter
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Cosmology
-

How to calculate redshift from the schwartzchild metric
Homework Statement I'm doing a project on the redshift from a star system (I chose a binomial system because why not). I might be going a little overboard using topology to calculate redshift, but whatever. First off, can I just treat a binomial system as the superposition of 2 sources which...- BiGyElLoWhAt
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
T
B Hubble breaks the distance record with a redshift of 11.1
Hubble breaks the distance record, with a large jump to a redshift of 11.1 Does this mean that some of theories need revision? We do not appear to reaching a limiting value!http://sci.esa.int/hubble/57530-hubble-breaks-cosmic-distance-record-heic1604/ -
How is the redshift of gravitational wave events measured?
LIGO reported the announced event with a redshift of 0.6 < z < 1.3. With no em radiation event reported (AFAIK), does anyone know how they have determined the redshift? I understand how they could measure the pre-merger, chirp and ring-down frequencies with good accuracy. In order to determine... -

Question on gravitational waves and redshift in BH coalesce
Dear Sirs My question relates to the recent observation of gravitational waves by LIGO. The paper PRL 116 "Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger -B.P Abbott et al"" depicts the chirp signal of the wave detected, where it is seen how both frequency and amplitude...- Javier Zapater
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Cosmology
-
C
Is There Evidence for Redshift Drift in High-z Galaxies?
I am interested in locating information of the evidence of z evolution that has been collected of the spectra of relatively high z sources over the previous 75(35) years. Before I get too far into the question, I thought I would try to find what research might have been done on the subject...- ConformalGrpOp
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
N
Measuring space expansion without redshift
Hi, Apart from the redshift of electromagnetic waves (which we do observe), is there any other evidence of space expansion that is not based on redshift? If not, is there a theoretical experiment that could let us observe and measure space expansion? Here I am assuming that space is not just... -
G
Solar Sail/ Mirror Redshift & Blueshift
Hi all, I was hoping you could help me out with this one. Im trying to calculate the redshift or blueshift of a photon that strikes a mirror and reflects. I know E=pc, and that 2p is the momentum transfer. I also know that kinetic energy is 2p/M (of the mirror). However, this says that...- God Plays Dice
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
T
Spectroscopy and the doppler effect
So the prof shows us how to tell if an object is red shifted, by comparing two spectra (i assume of the same object). The emission lines had similar gaps but were shifted right, therefore moving away from us. How can you obtain two different spectra of the same object if it's constantly moving...- The Subject
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

Question about Recombination Redshift values
Wikipedia gives the redshift of recombination at z = 1500 (roughly 4,000 K). The Plank report list a 'redshift for which the optical length equals unity' and gives a value of 1090. What is the difference between the two?- Dr. Strange
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Recombination Redshift
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Cosmology