- #1
samy4408
- 62
- 9
- Homework Statement
- my answer is an image in the post
- Relevant Equations
- no particular equations
Hello i am trying to solve a problem set about chemical equilibrium , the issue is that my results don't correspond to the correction . can someone tell me what is wrong with my answer , thanks
here is the problem and his correction :
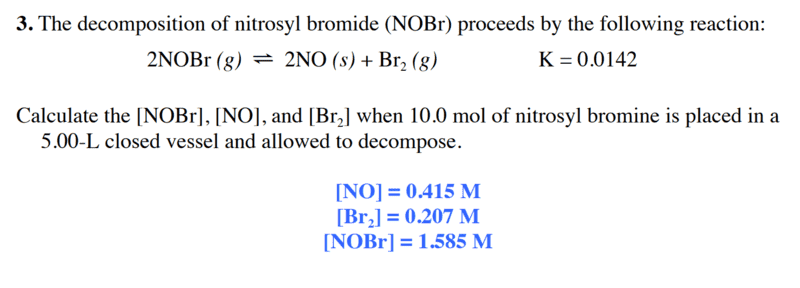
here is my answer :
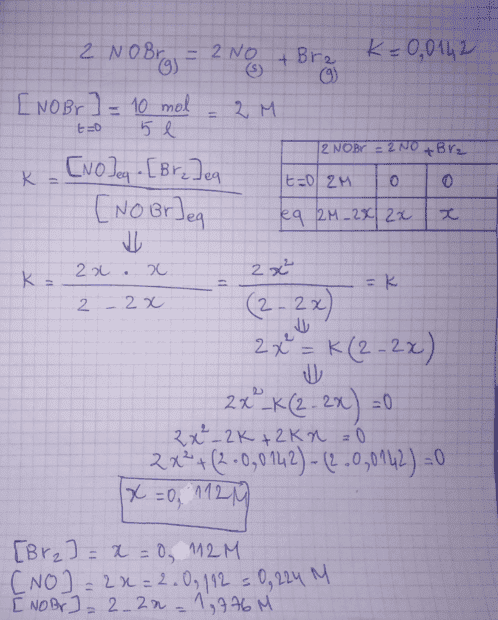
here is the problem and his correction :
here is my answer :