- #1
Dell
- 590
- 0
for the beam in the diagram
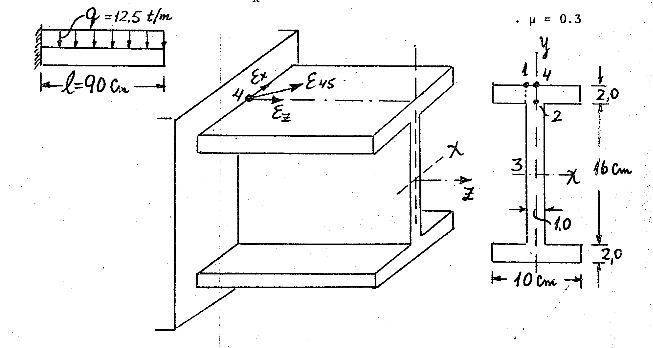
E=2.1e6kg/cm2
Ixx=3600cm4
find:
the principle stresses in the beam
the strains ex, ez e(45) found on the strain rosette placed at point 4
i have only managed to find the principle stress z which i found at point 1 --- 1406kg/cm2 where would i find the other stresss? how can i find the stress on the x axis? to find z i used -Y*M/I knowing that the maximum moment is at the wall and is -5.0625[t*m]
to find the strains i just divide by E and i get the z strain=6.67e-4 how can i find the x strain? once i find the x strain can i say the shear strain is 0?
E=2.1e6kg/cm2
Ixx=3600cm4
find:
the principle stresses in the beam
the strains ex, ez e(45) found on the strain rosette placed at point 4
i have only managed to find the principle stress z which i found at point 1 --- 1406kg/cm2 where would i find the other stresss? how can i find the stress on the x axis? to find z i used -Y*M/I knowing that the maximum moment is at the wall and is -5.0625[t*m]
to find the strains i just divide by E and i get the z strain=6.67e-4 how can i find the x strain? once i find the x strain can i say the shear strain is 0?