- #1
Amaelle
- 310
- 54
Summary:: trying to calculate the torsion but couldn´t understand the solution
Greetings
I´m trying to understand why the multiplied the Force by a/2 to find the torsion in te point c
thank you!
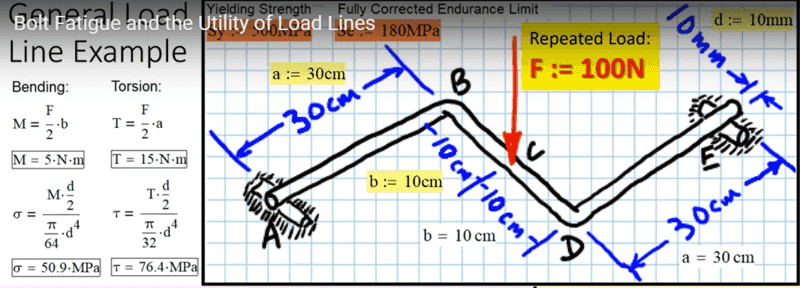
Greetings
I´m trying to understand why the multiplied the Force by a/2 to find the torsion in te point c
thank you!