- #1
physstudent189
- 2
- 0
- Homework Statement
- The figure below shows a thin converging lens for which the radii are R1 = 8.48 cm and R2 = -11.4 cm. The lens is in front of a concave spherical mirror of radius R = 6.07 cm. If its focal points F1 and F2 are 4.58 cm from the vertex of the lens: b) If the lens and mirror are 20.3 cm apart and an object is placed 8.00 cm to the left of the lens, determine the position of the final image relative to the lens (Positive values are to the left).
- Relevant Equations
- 1/f = 1/do + 1/di
I created the following ray diagram to help me solve the problem:
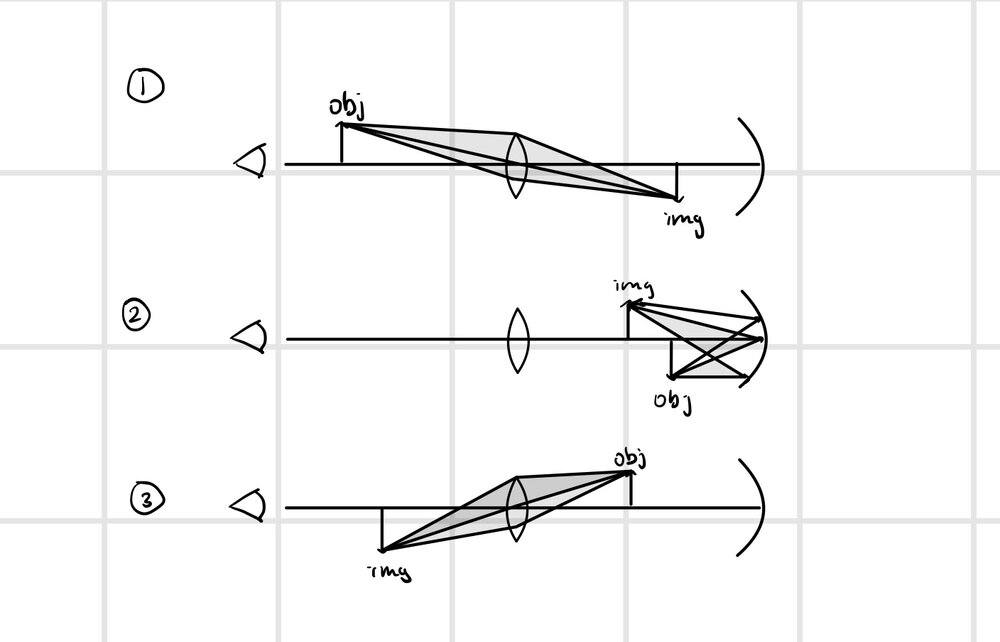
Then I applied the mirror equation 3 separate times.

However, the final image distance I got is wrong. I'm wondering if I'm mistaken in taking the last object distance to be negative. However I only have one more try to get this right so I really want to make sure I'm approaching it from the right angle. I thought the last image distance would be negative because it is distance behind the converging lens, and we are told in the question that distances to the left of the lens (in front) are positive. I really appreciate any help or pointers anyone can give. Thank you!
Then I applied the mirror equation 3 separate times.
However, the final image distance I got is wrong. I'm wondering if I'm mistaken in taking the last object distance to be negative. However I only have one more try to get this right so I really want to make sure I'm approaching it from the right angle. I thought the last image distance would be negative because it is distance behind the converging lens, and we are told in the question that distances to the left of the lens (in front) are positive. I really appreciate any help or pointers anyone can give. Thank you!