- #1
unscientific
- 1,734
- 13
I'm utterly confused by co-moving distance, transverse comoving distance and proper distance. Is comoving distance = proper distance? Then what is transverse comoving distance? Here's what I know so far:
The FRW metric can either be expressed as
[tex]ds^2 = c^2dt^2 - a^2(t) \left[ \frac{dr^2}{1-kr^2} + r^2(d\theta^2 + sin^2 \theta d\phi^2) \right] [/tex]
or can be expressed as
[tex]ds^2 = c^2dt^2 - a^2(t) \left[ d\chi^2 + S^2(\chi) (d\theta^2 + sin^2 \theta d\phi^2) \right] [/tex]
Hobson describes: "##(\chi, \theta, \phi)## and ##(r,\theta,\phi)## are co-moving coordinates, where the galaxy has fixed coordinate positions were the 'cosmological fluid' is at rest. He also says that luminosity distance ##d_L = (1+z) R_0 S(\chi)## and angular diameter distance ##d_A = \frac{R_0 S(\chi)}{1+z}##.
My notes describe them as
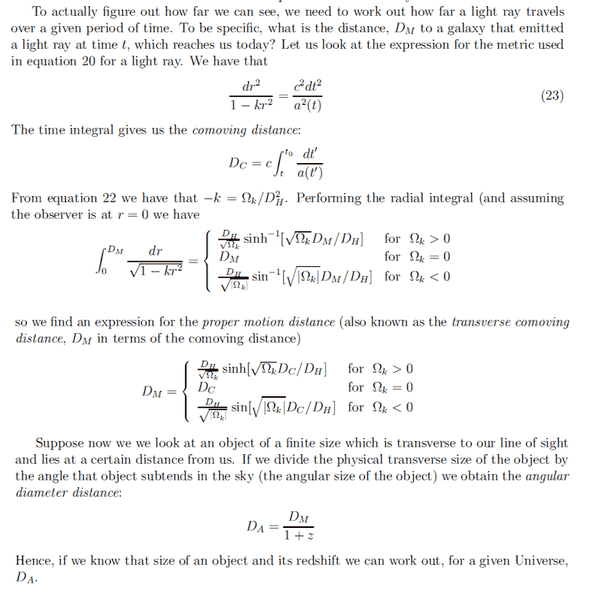
To reconcile both material, it seems that proper motion distance is ##D_M = R_0 S(\chi)## and proper distance = ##D_C## which is path taken by light?
The FRW metric can either be expressed as
[tex]ds^2 = c^2dt^2 - a^2(t) \left[ \frac{dr^2}{1-kr^2} + r^2(d\theta^2 + sin^2 \theta d\phi^2) \right] [/tex]
or can be expressed as
[tex]ds^2 = c^2dt^2 - a^2(t) \left[ d\chi^2 + S^2(\chi) (d\theta^2 + sin^2 \theta d\phi^2) \right] [/tex]
Hobson describes: "##(\chi, \theta, \phi)## and ##(r,\theta,\phi)## are co-moving coordinates, where the galaxy has fixed coordinate positions were the 'cosmological fluid' is at rest. He also says that luminosity distance ##d_L = (1+z) R_0 S(\chi)## and angular diameter distance ##d_A = \frac{R_0 S(\chi)}{1+z}##.
My notes describe them as
To reconcile both material, it seems that proper motion distance is ##D_M = R_0 S(\chi)## and proper distance = ##D_C## which is path taken by light?
Last edited: