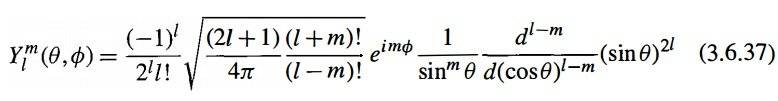- #1
davidge
- 554
- 21
Hi everyone. I'm looking for a derivation of the Spherical Harmonics that result in the form below given in Sakurai's book. I looked up on web and I found just that these are related with Legendre Polynomials. Has anyone a source, pdf, or similar to indicate me? (I would appreciate a derivation that uses the same notation as Sakurai.)