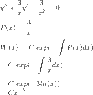- #1
Fatima Hasan
- 319
- 14
Homework Statement
[/B]
Homework Equations
##W(x) = C exp (∫ P(x) dx)##
##y''+P(x)y'+g(x)=0##
The Attempt at a Solution
Divide the origin equation by (x) to get the standard form of the homogeneous equation :
##y'' +\frac{3y'}{x} - \frac{3y}{x}##
##P(x) = \frac{3}{x}##
## exp (- ∫ \frac{3}{x}##
## = exp ( -3 ln (x))##
## = x^{-3}##
##W(x) = C x^{-3} ##
Could someone check my answer please?