- #1
Davyd Sadovskyy
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
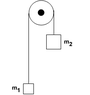
In the system below, m1<m2. When the object of mass m2 has descended a distance h, the potential energy of the system has decreased by:
Homework Equations
the answer is (m2-m1)gh
The Attempt at a Solution
I used ΔU= Uf-Ui
m1gh-m2gh=ΔU (I think that the decrease in potential energy is equal to the change in Ug because at the final configuration, m1 is at the same height that m2 is at initially, but has less weight, so the potential energy must decrease from start to finish)
gh(m1-m2)
why does the answer have the two masses in reversed order. pls help