- #1
Tone L
- 73
- 7
Greetings. I have a system that is powered by 5V . You will see below in the image. The system displays the difference between the Hi and Lo signal digitally, on the display which the board is plugged into. However. I want to store the data maybe in a SD card? Using Arduino? How do I harness the Hi Lo signal?
I am looking for circuit board recommendations i think.
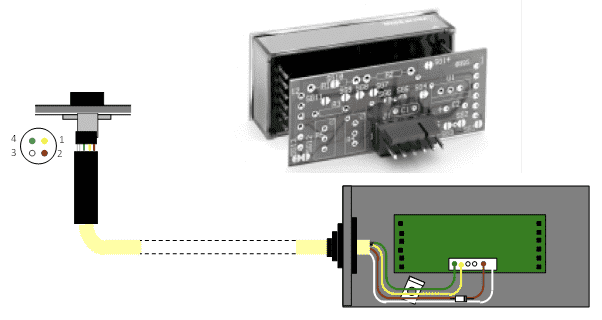
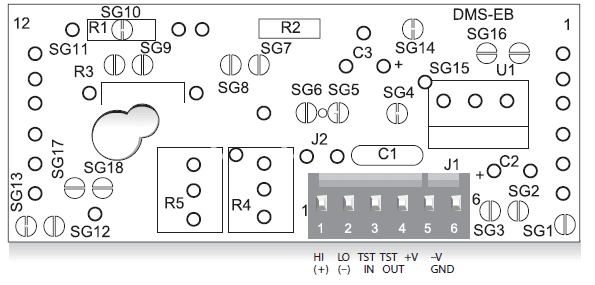
I am looking for circuit board recommendations i think.