- #1
htoo
- 1
- 0
Could someone please explain me how can we get equation 5.177?
Thank you so much for your help
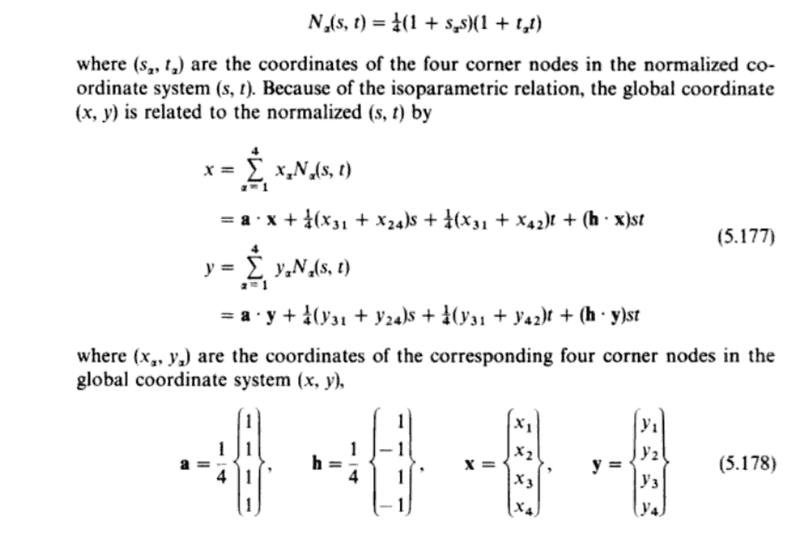
Thank you so much for your help
FEM hourglass control 2D is a method used in finite element analysis to prevent the artificial hourglassing phenomenon that can occur in 2D simulations. Hourglassing is when elements in the simulation show an hourglass-like deformation, which can cause inaccurate results and instability.
FEM hourglass control 2D is important because it helps to improve the accuracy and stability of finite element simulations. It can prevent incorrect results and reduce the risk of numerical instabilities that can occur without this control method.
FEM hourglass control 2D works by applying an artificial stiffness to the elements in the simulation that are prone to hourglassing. This stiffness helps to distribute the deformation more evenly and prevents hourglass-like deformations from occurring.
One limitation of FEM hourglass control 2D is that it is only effective in 2D simulations. It may not be as effective in 3D simulations, and other methods may need to be used. Additionally, FEM hourglass control 2D may increase the computational time and complexity of the simulation.
Yes, there are alternative methods to control hourglassing in finite element simulations. Some examples include selective reduced integration, hourglass energy minimization, and hourglass stabilization. The choice of method depends on the specific simulation and its requirements.