- #1
chunhui219
- 4
- 0
How to calculate gate resistance, Rg in the JFET amplifier circuit?
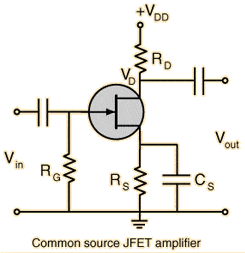
And What is the function of Rg?
And What is the function of Rg?
Last edited:
A gate resistor, or Rg, is used in JFET circuits to limit the current flowing into the gate terminal. It also helps to prevent oscillations and improve stability in the circuit.
The value of gate resistor is typically determined by the maximum gate current specified by the JFET's datasheet. It is recommended to choose a value that is at least 10 times higher than the maximum gate current.
Yes, a JFET circuit can function without a gate resistor. However, it is not recommended as it may cause instability and potential damage to the JFET. A gate resistor is considered good design practice for JFET circuits.
If the value of gate resistor is too high, it may limit the gate current too much and result in a decrease in circuit gain. It may also cause the JFET to operate in a non-linear region, affecting the overall performance of the circuit.
Yes, the gate resistor value should also take into account the input impedance of the JFET and the desired bias point. It is recommended to consult the JFET's datasheet and use a resistor value that provides a good balance between gate current limiting and circuit performance.