- #1
Raihan amin
- 46
- 0
OP warned about not using the homework template
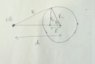
Two identical metalic spherical conductor of radii ##R## are at a distance ##d## apart.One of the conductor has charge ##Q## while the another one is neutral.What will be the induced charge on the other conductor ?
If we put an image charge ##q## inside the neutral one. Then the potential at the surface is $$V = {\frac {Q} {r_1} }+\frac {q}{r_2}$$
So $$V=\frac {Q}{\sqrt {R^2 +d^2 -2Rdcos {\theta}}} + \frac {q}{\sqrt {R^2 + d'^2 - 2Rd' cos{\theta}}} $$
Now I know that the suface of the spherical conductor will be equipotential,independent of ##\theta##
Here i consider the other charge as a point particle.but I can't find V.Still i don't know whether the image charge method will do or not.
Please help me someone to find it.Thanks.
If we put an image charge ##q## inside the neutral one. Then the potential at the surface is $$V = {\frac {Q} {r_1} }+\frac {q}{r_2}$$
So $$V=\frac {Q}{\sqrt {R^2 +d^2 -2Rdcos {\theta}}} + \frac {q}{\sqrt {R^2 + d'^2 - 2Rd' cos{\theta}}} $$
Now I know that the suface of the spherical conductor will be equipotential,independent of ##\theta##
Here i consider the other charge as a point particle.but I can't find V.Still i don't know whether the image charge method will do or not.
Please help me someone to find it.Thanks.
Attachments
Last edited: