- #1
Drao92
- 72
- 0
When you shift step function u(t-a), is it true for a<0?
Im sorry but we did only exercises when you don't have to use this and in my homework using this is the only way i can solve it.
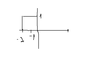
Like in this pic. Isnt x(t) (forgot to mark the axis, sorry) x(t)=u(t+2)-u(t)?
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=57584&stc=1&d=1365341968
Im sorry but we did only exercises when you don't have to use this and in my homework using this is the only way i can solve it.
Like in this pic. Isnt x(t) (forgot to mark the axis, sorry) x(t)=u(t+2)-u(t)?
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=57584&stc=1&d=1365341968