- #1
EEristavi
- 108
- 5
Homework Statement
This is the problem from the book "physics for scientists and engineers..." by Serway, Jewett / Chapter 5, problem 98
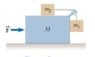
Initially, the system of objects shown in Figure P5.93 -
is held motionless. The pulley and all surfaces and wheels
are frictionless. Let the force F be zero and assume
that m1 can move only vertically. At the instant after
the system of objects is released, find (a) the tension T
in the string, (b) the acceleration of m2, (c) the acceleration
of M, and (d) the acceleration of m1. (Note: The
pulley accelerates along with the cart.)
Figure P5.93 description:
there is a block with mass M, above it - another block is placed (with the mass m2), and this is connected to the block-m1 by string (over the pulley)
Note: There is an attached the image also.
Homework Equations
Newton's second law
The Attempt at a Solution
My only question is:
Why does the "main block" accelerates - if we don't have a friction and F=0
my guess is that, there is a mistake
am I right or wrong (if wrong why)?