- #1
PhysicsTest
- 238
- 26
- TL;DR Summary
- To understand the logic of phase current measurement in 3 phase AC motors using shunt resistors from a reference application note.
I have seen an application note of how to measure the phase currents using shunt resistors as shown below
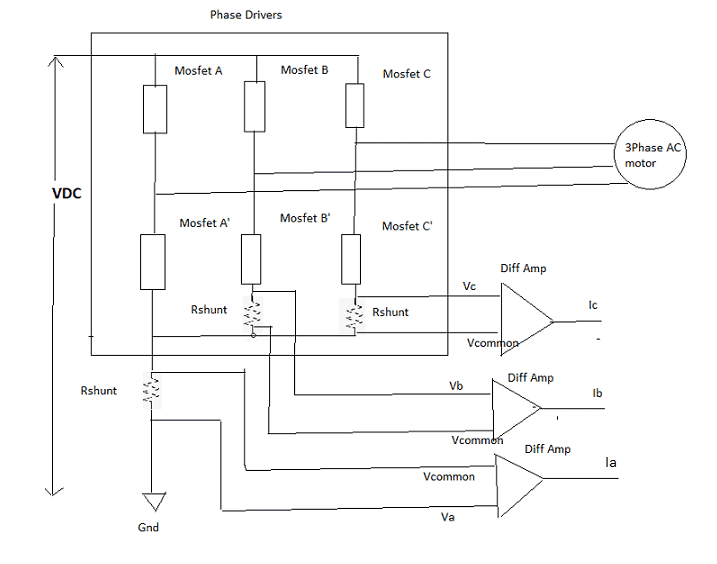
I am only confused with the connection when measuring the phase Ia current, it differs from the way the shunt resistor is connected for Ic and Ib, he could have done the same way like Ib and Ic. Is there any advantage doing like this? By using Ia he was also able to detect the fault in the phase currents? My question is what are the conditions under which the phase currents can be wrong like one condition i can think of is
a. Ia+Ib+Ic ##\neq ## 0.
I am only confused with the connection when measuring the phase Ia current, it differs from the way the shunt resistor is connected for Ic and Ib, he could have done the same way like Ib and Ic. Is there any advantage doing like this? By using Ia he was also able to detect the fault in the phase currents? My question is what are the conditions under which the phase currents can be wrong like one condition i can think of is
a. Ia+Ib+Ic ##\neq ## 0.