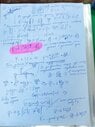- #1
DaraRychenkova
- 1
- 0
- Homework Statement
- - Determination of the dipole (p=ql). Find the dipole potential at a distance r much larger than the size of the dipole itself. Calculate the field of the dipole using the relationship between the potential and the field.
1. Solve the problem of finding the dipole field using the expression for the potential obtained in the previous problem in polar coordinates
- Relevant Equations
- Dipole, electrostatic
I don't know how to get the result referring to the previous task. Is my decision correct?