- #1
Muh. Fauzi M.
- 17
- 1
I have a problem when trying to proof orthogonality of associated Laguerre polynomial. I substitute Rodrigue's form of associated Laguerre polynomial :
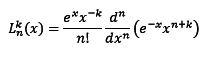
to mutual orthogonality equation :
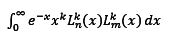
and set, first for
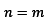 and second for
and second for
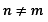 .
.
But after some step, I get trouble with this stuff :
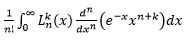
I've already search solution for this form but still no light. Any body here could help?
and set, first for
But after some step, I get trouble with this stuff :
I've already search solution for this form but still no light. Any body here could help?