- #1
lightlightsup
- 95
- 9
- Homework Statement
- If the block is pulled slightly down the incline and released, what is the period of the resulting oscillations?
- Relevant Equations
- See images.
Why doesn't the incline angle play a role in changing the ##m## component of this equation?
##T = 2π\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}##
FOR QUESTION 25, PART B:
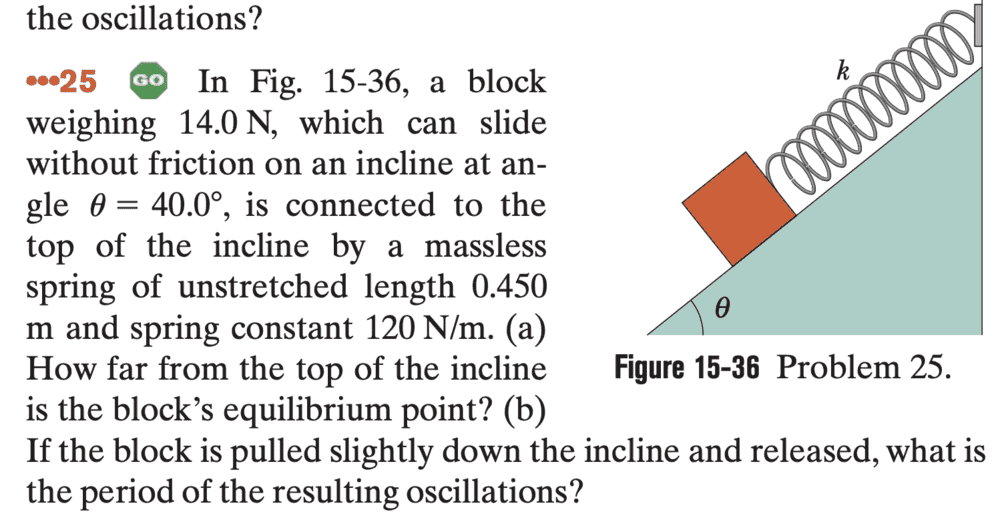
ANSWER:
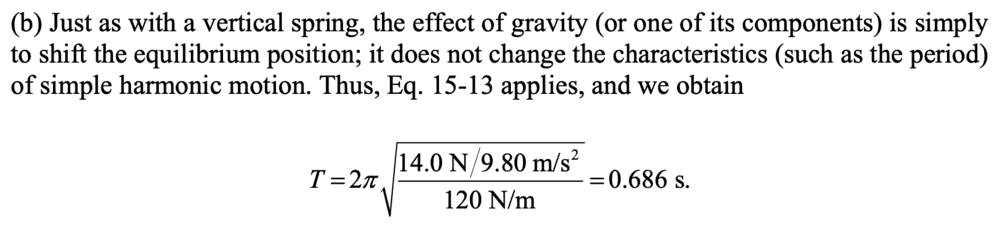
##T = 2π\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}##
FOR QUESTION 25, PART B:
ANSWER: