- #1
Jason-Li
- 119
- 14
- Homework Statement
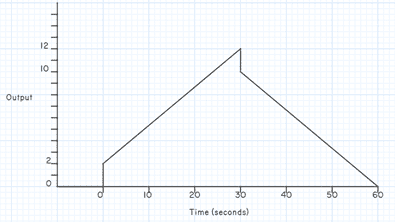
- FIGURE 6 shows a proportional plus derivative controller that has a proportional band of 20% and a derivative action time of 0.1 minutes. Construct the shape of the output waveform for the triangular input waveform shown, if the input rises and falls at the rate of 4 units per minute.
- Relevant Equations
- None required
Hello,
There is a thread related to this question however it was marked correct but doesn't look correct to me?
https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/step-change-in-a-proportional-plus-integral-controller.961180/
I think I have it but it is quite different to other answers I have seen?
I have found
PB=20% hence gain=5
dAT = 0.1min = 6s
Would rise and peak at 2units at 30s however due to gain this will be 10units, hence change due to derivative would be:
10/30 * 6s = 2units, then once peaked at 30s it would reduce by the same derivative and create the following graph:
There is a thread related to this question however it was marked correct but doesn't look correct to me?
https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/step-change-in-a-proportional-plus-integral-controller.961180/
I think I have it but it is quite different to other answers I have seen?
I have found
PB=20% hence gain=5
dAT = 0.1min = 6s
Would rise and peak at 2units at 30s however due to gain this will be 10units, hence change due to derivative would be:
10/30 * 6s = 2units, then once peaked at 30s it would reduce by the same derivative and create the following graph: