- #1
ilovescience85
- 25
- 0
Homework Statement
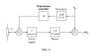
FIGURE 9 shows the block diagram of the control of an electric heatingsystem. The heater is driven from a voltage-controlled power supply, the
voltage V1 being derived from a potientiometer. The output temperature,
θO, is subject to disturbances, θD, because of changes in the ambient
temperature. It is proposed to apply 'disturbance feedback control' to the
system by the inclusion of a transducer that measures the external
temperature and feeds a signal back to the input via a proportional
controller of gain H.
Determine the required value of H to eliminate the effect of the disturbance.
Homework Equations
Unsure
The Attempt at a Solution
Unsure where to start.