- #1
milkism
- 117
- 15
- Homework Statement
- Find the impuls wavefunction phi(p) from the position wavefunction.
- Relevant Equations
- Look solution.
I have this following Gaussian wavefunction.
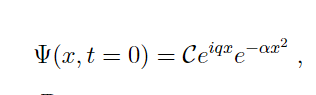
I found the constant C to be $$\sqrt{\sqrt{\frac{2 \alpha}{\pi}}}$$.
Now they're asking me to find the normalized impuls wavefunction $$\phi(p)$$. I tried to use the fourier transform relation
$$\phi (p) = \int e^{-\frac{i ( p x)}{\hbar}} \Psi (x,t=0) dx$$
and i got a long answer
$$\sqrt{\sqrt{\frac{2 \alpha}{\pi}}} \sqrt{\frac{\pi}{\alpha}} e^{-\frac{q^2}{4\alpha} + \frac{pq}{2 \alpha \hbar} - \frac{p^2}{4 \alpha \hbar ^2}}$$
Is there an other way to solve this? Because next question is to find the expectation value of position from the normalized impuls wavefunction, which is going to be very hard.
I found the constant C to be $$\sqrt{\sqrt{\frac{2 \alpha}{\pi}}}$$.
Now they're asking me to find the normalized impuls wavefunction $$\phi(p)$$. I tried to use the fourier transform relation
$$\phi (p) = \int e^{-\frac{i ( p x)}{\hbar}} \Psi (x,t=0) dx$$
and i got a long answer
$$\sqrt{\sqrt{\frac{2 \alpha}{\pi}}} \sqrt{\frac{\pi}{\alpha}} e^{-\frac{q^2}{4\alpha} + \frac{pq}{2 \alpha \hbar} - \frac{p^2}{4 \alpha \hbar ^2}}$$
Is there an other way to solve this? Because next question is to find the expectation value of position from the normalized impuls wavefunction, which is going to be very hard.
