- #1
Arnsol
- 2
- 0
- Homework Statement
- w
- Relevant Equations
- See attepmt
Hello,
So we are designing a turbine. We have a shaft that receives 710W / 13.6NM / 500RPM from the runner and we are going to find a diameter with safety factor of 3.
Take the following information regarding metal:
Aluminium 6061
i know F.O.S = Max load / Load applied.
Still i can't wrap my mind around which of those i should use. First thought is going with the 48 MPA yield since aluminium is ductile?
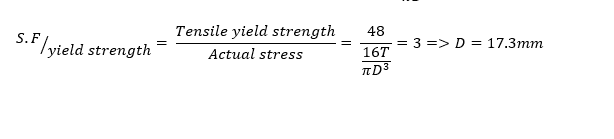
Any thoughts? I am so confused...
So we are designing a turbine. We have a shaft that receives 710W / 13.6NM / 500RPM from the runner and we are going to find a diameter with safety factor of 3.
Take the following information regarding metal:
Aluminium 6061
| Tensile strength | 115 MPa | |
| Yield strength | 48 MPa | |
| Shear strength | 83 MPa | |
| Fatigue strength | 62 MPa |
Still i can't wrap my mind around which of those i should use. First thought is going with the 48 MPA yield since aluminium is ductile?
Any thoughts? I am so confused...