- #1
Buzz Bloom
Gold Member
- 2,519
- 467
It has occurred to me that the Friedmann equation
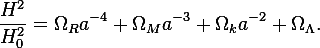
allows for a solution
H = H0 = 0 .
This seems to say that independently of the value of the scale factor a, and the various Ωs, a static universe is possible. I am guessing that this solution is spurious and is a side effect of the derivation of the equation.
I am curious about how the derivation introduced this spurious solution of the cosmological form of the GR equations, and would much appreciate someone posting an explanation.
Regards,
Buzz
allows for a solution
H = H0 = 0 .
This seems to say that independently of the value of the scale factor a, and the various Ωs, a static universe is possible. I am guessing that this solution is spurious and is a side effect of the derivation of the equation.
I am curious about how the derivation introduced this spurious solution of the cosmological form of the GR equations, and would much appreciate someone posting an explanation.
Regards,
Buzz