- #1
minifhncc
- 46
- 0
Series shunt or series series??
Hello,
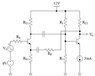
I'm having trouble in general determining the feedback topologies...
My guess is that this is series-series since the source is in series with Rf and since setting io=0 for the output loop disables Vf... But I'm not sure... Could someone please tell me if I'm correct or not...
A good method in determining the topologies would be also appreciated.
Thanks in advanced
Hello,
I'm having trouble in general determining the feedback topologies...
My guess is that this is series-series since the source is in series with Rf and since setting io=0 for the output loop disables Vf... But I'm not sure... Could someone please tell me if I'm correct or not...
A good method in determining the topologies would be also appreciated.
Thanks in advanced