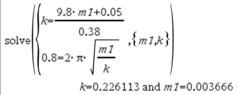- #1
torinketo
- 2
- 1
- Homework Statement
- A block of unknown mass is attached to the end of a vertical spring. When a second 50 g block is suspended, the spring extends by 38 cm. The oscillation period without the second 50 g block is 0.8 s. Find:
(a) the spring constant of the spring (in N/m);
(b) the mass of the first block (in kg).
- Relevant Equations
- T=2pi*sqrt(m/k)
k=mg/x
m1 = unknown
m2 = 0.05 kg
x = 0.38 m
T = 0.8s
Tried to plug in values into the above equations:
0.8 = 2pi*sqrt(m1+0.05/k)
k = ((m1+0.05)*9.8)/0.38
Got negative values for both k and m which doesn't make sense
m2 = 0.05 kg
x = 0.38 m
T = 0.8s
Tried to plug in values into the above equations:
0.8 = 2pi*sqrt(m1+0.05/k)
k = ((m1+0.05)*9.8)/0.38
Got negative values for both k and m which doesn't make sense