- #1
soccer4life
- 13
- 0
1. Problem Statement
Find the steady state output yss(t) for the input u(t)=t-π in terms of an infinite sum of sinusoids.
We are given the transfer function as:
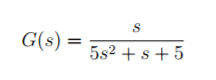
2. Homework Equations
G(i) = ...
|G(ik)| = ...
Φ(ik) = ... (this is the angle)
yss(t) = βk||G(ik)|ei(kt+Φ(ik)) ***check that this is the correct formula please***
3. Attempt at Solution
I've found the following:
G(i)=1
|G(ik)| =
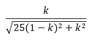 (Any tips/tricks on how to input fractions/square roots into PF would be greatly appreciated...)
(Any tips/tricks on how to input fractions/square roots into PF would be greatly appreciated...)
Φ(ik) =
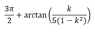
Previously, the Fourier Series expansion was found, and is: the sum from 1 to infinity of Σ-2sin(kt)/k
I know that these values are right. However, I don't fully understand how to incorporate them into the steady state formula (assuming that my formula is correct)
Find the steady state output yss(t) for the input u(t)=t-π in terms of an infinite sum of sinusoids.
We are given the transfer function as:
2. Homework Equations
G(i) = ...
|G(ik)| = ...
Φ(ik) = ... (this is the angle)
yss(t) = βk||G(ik)|ei(kt+Φ(ik)) ***check that this is the correct formula please***
3. Attempt at Solution
I've found the following:
G(i)=1
|G(ik)| =
Φ(ik) =
Previously, the Fourier Series expansion was found, and is: the sum from 1 to infinity of Σ-2sin(kt)/k
I know that these values are right. However, I don't fully understand how to incorporate them into the steady state formula (assuming that my formula is correct)
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: