- #1
foadsf
I have also asked this question in SO and CFD online
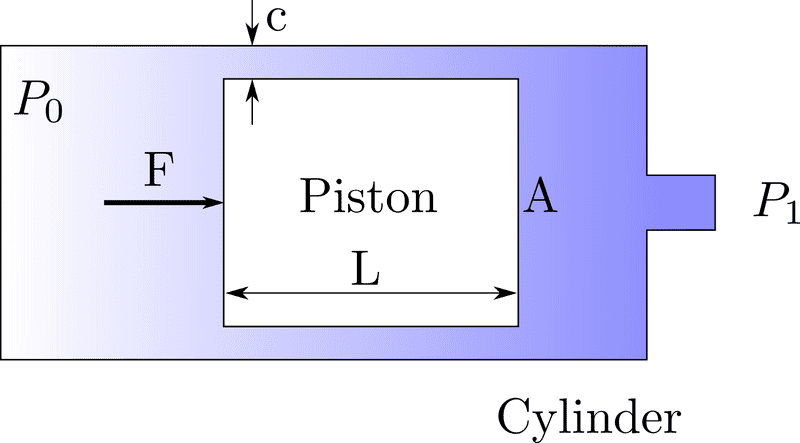
Assuming that we have a pneumatic cylinder-piston with arbitrary but known surface area A, a known clarence c, and a known length L. What is the best model to describe the total steady state force applied on the piston considering the leakage? (the force required to keep the piston in place)
 What I'm looking for is an equation in the form of $F=f\left(P_1,A, L, c\right)$. In extreme cases:
What I'm looking for is an equation in the form of $F=f\left(P_1,A, L, c\right)$. In extreme cases:
- if ## c\rightarrow 0 ## then ##F=P_1A## is just hydrostatic pressure
- if c is big then ##F\approx \frac{1}{2}\rho\nu^2C_DA## is just air drag
I can calculate leakage from empirical or theoretical models but I don't know how to proceed from there.
Assuming that we have a pneumatic cylinder-piston with arbitrary but known surface area A, a known clarence c, and a known length L. What is the best model to describe the total steady state force applied on the piston considering the leakage? (the force required to keep the piston in place)
- if ## c\rightarrow 0 ## then ##F=P_1A## is just hydrostatic pressure
- if c is big then ##F\approx \frac{1}{2}\rho\nu^2C_DA## is just air drag
I can calculate leakage from empirical or theoretical models but I don't know how to proceed from there.
