- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Transistors: Tiny Silicon Crystals, Memory Cells, & Shrinking Bits
In summary, transistors are small crystals of silicon used in memory cells and switches. A single memory chip can hold more than 4 transistors, with larger chips holding millions or even billions. The term "shrinking bit" may refer to the number of atoms needed to store 1 bit of data. The diagram provided may perform similar operations as a memory cell, but with hidden circuit complexity. The number of memory cells a chip can hold can be calculated, but it should be noted that DRAM does not use a 4-transistor cell, instead storing information in a capacitor.
Engineering news on Phys.org
- #2
davenn
Science Advisor
Gold Member
2023 Award
- 9,590
- 10,269
hi there
welcome to PF
all your questions could have been answered on google
here's something to get you started.....
a few more than that ....
eg.
a 64Mb Dynamic RAM chip has over 67 million transistors on it
a 1Gb Dynamic RAM chip has over 1 billion transistors on it
not 100% sure of what you are referring to ... maybe this ...
the number of atoms of material needed to be able to store 1 bit of dataDave
welcome to PF
all your questions could have been answered on google
here's something to get you started.....
nabil__ said:A single memory chip can hold up to 4 transistor ?
a few more than that ....
eg.
a 64Mb Dynamic RAM chip has over 67 million transistors on it
a 1Gb Dynamic RAM chip has over 1 billion transistors on it
nabil__ said:What is the shrinking bit ?
not 100% sure of what you are referring to ... maybe this ...
the number of atoms of material needed to be able to store 1 bit of dataDave
- #3
nabil__
- 7
- 0
davenn said:hi there
welcome to PF
all your questions could have been answered on google
here's something to get you started.....
a few more than that ....
eg.
a 64Mb Dynamic RAM chip has over 67 million transistors on it
a 1Gb Dynamic RAM chip has over 1 billion transistors on it
not 100% sure of what you are referring to ... maybe this ...
the number of atoms of material needed to be able to store 1 bit of dataDave
- #4
- #5
nabil__
- 7
- 0
davenn said:
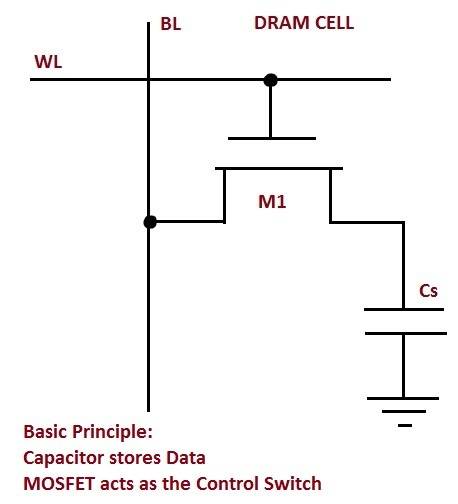
Yes. Is the following diagram ( attached ) performs operation with the previous diagram attached ?
How and why ?
Attachments
- #6
- #7
nabil__
- 7
- 0
How to calculate that how many memory cell a memory chip can hold ?
- #8
Svein
Science Advisor
- 2,298
- 796
DRAM does not use a 4-transistor cell, they store the information in a capacitor.
1. What is a transistor and how does it work?
A transistor is a tiny semiconductor device made of silicon that acts as a switch or amplifier for electronic signals. It consists of three layers of silicon with different electrical properties, namely the emitter, base, and collector. When a small current is applied to the base, it controls the larger current flowing between the emitter and collector, thus allowing the transistor to amplify or switch signals.
2. What is the significance of silicon crystals in transistors?
Silicon crystals are the most commonly used material in transistors due to their semiconductor properties. Silicon atoms have four valence electrons, which makes it easy to form the required layers of the transistor. Additionally, silicon crystals can be easily modified and doped to alter its electrical properties, making it an ideal material for transistors.
3. How are transistors used in memory cells?
In memory cells, transistors are used as switches to store and retrieve data in the form of binary bits. Each transistor represents a bit, and by turning them on or off, the computer can store and retrieve data. The tiny size of transistors allows for more memory cells to be packed into a smaller space, leading to the development of more powerful and compact devices.
4. What is the role of shrinking bits in transistors?
Shrinking bits refer to the continuous miniaturization of transistors, which has been a key factor in the advancement of technology. As transistors shrink in size, more of them can be packed into a smaller space, leading to faster and more powerful devices. Shrinking bits also help in reducing the cost of production, making technology more accessible to the masses.
5. What are some challenges in shrinking bits in transistors?
One of the biggest challenges in shrinking bits is facing the limitations of Moore's Law, which states that the number of transistors on a chip will double approximately every two years. As transistors reach the atomic scale, they start to exhibit quantum effects, making it difficult to control the flow of electrons. This has led to the exploration of new materials and technologies to overcome this limitation and continue the trend of shrinking bits in transistors.
Similar threads
-
Atomic and Condensed Matter
- Replies
- 19
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 14
- Views
- 3K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 3K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
-
Computing and Technology
- Replies
- 14
- Views
- 3K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 858
Share: