- #1
Lay1
- 44
- 7
- Homework Statement
- Refer to the figure. Assume the green LED drops 2V across it when it is on. The maximum current in the LED is to be set at 10mA and the minimum current is 2mA. Choose values for R1 and R2 to meet these requirements.
- Relevant Equations
- V=IR
Here is the figure mentioned above.
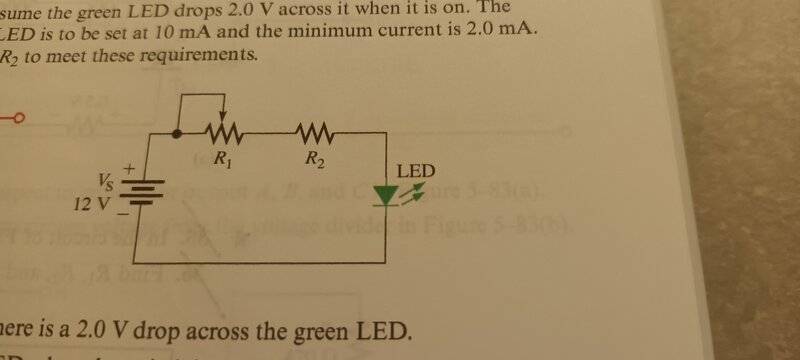
My thinking is that for maximum current, resistance must be minimum. Thus, R1 is not considered which means the voltage drop of R2 is 10V. So, R2 is 1kohm. For minimum, I=2mA, so R1+R2=5kohm, since R2 is 1kohm, R1 must be 4kohm. This is how I deduce. However, the answer shows that R1=5kohm while R2 is 1kohm. I do not understand why it is so. Could someone help me explain why? Thank you as always.
My thinking is that for maximum current, resistance must be minimum. Thus, R1 is not considered which means the voltage drop of R2 is 10V. So, R2 is 1kohm. For minimum, I=2mA, so R1+R2=5kohm, since R2 is 1kohm, R1 must be 4kohm. This is how I deduce. However, the answer shows that R1=5kohm while R2 is 1kohm. I do not understand why it is so. Could someone help me explain why? Thank you as always.
Last edited: