- #1
M_Abubakr
- 10
- 1
- TL;DR Summary
- I have a 2D unit cell which is a Repeated Unit Cell (RUC) of a composite with a fibre and a matrix. Longitudinal excitation is applied of different frequencies. Using Floquet-Blochs Theorem I have to get the dispersion curves for this composite unit cell.
How do I get the wave dispersion for a 2D continuum unit cell subjected to a periodic boundary which is excited longitudinally? I'll be applying forces in ABAQUS with varying frequencies. I have come across Blochs theorem but I can't find any application of it in continuous systems. Every application of it deals with atomic wave functions which I have no idea of how electron states are analogous to mechanical systems.
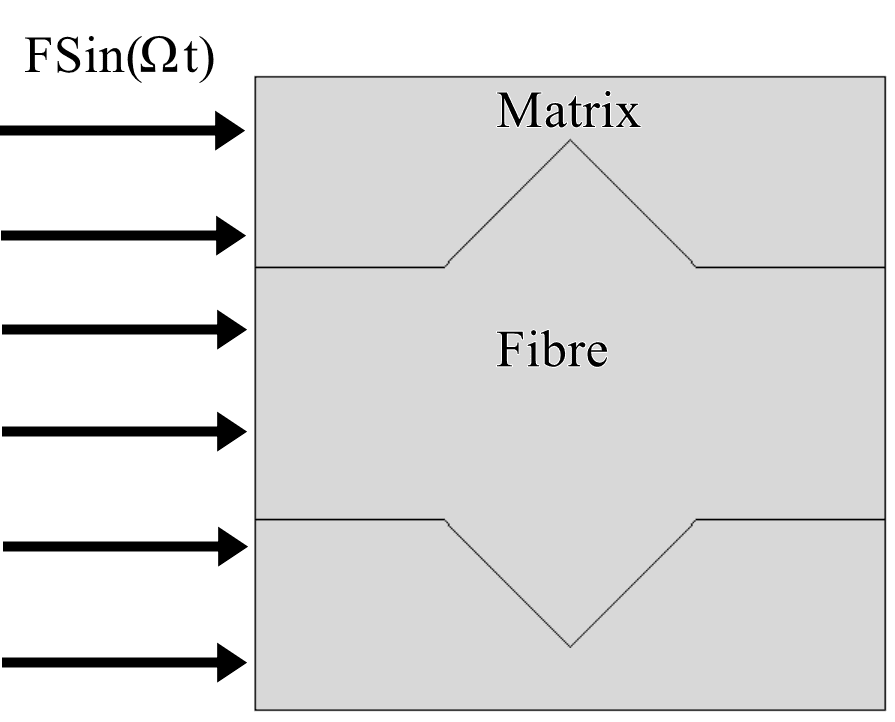
Can anyone tell me how to start the analysis? I already have the natural frequencies of the unit cell.
Can anyone tell me how to start the analysis? I already have the natural frequencies of the unit cell.