- #1
Mohmmad Maaitah
- 87
- 19
- Homework Statement
- As in picture
- Relevant Equations
- Work by gravity = -mgh
Shouldn't work be minus when the man climbing up and force on him is down?
shouldn't the power be also in minus?
Can someone explain to me why is it positive please!

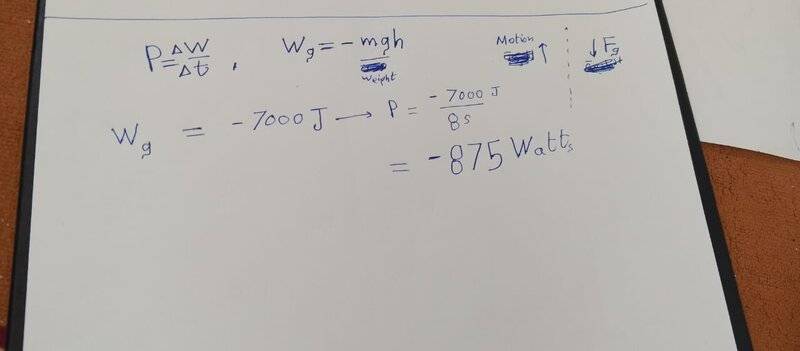
shouldn't the power be also in minus?
Can someone explain to me why is it positive please!