SUMMARY
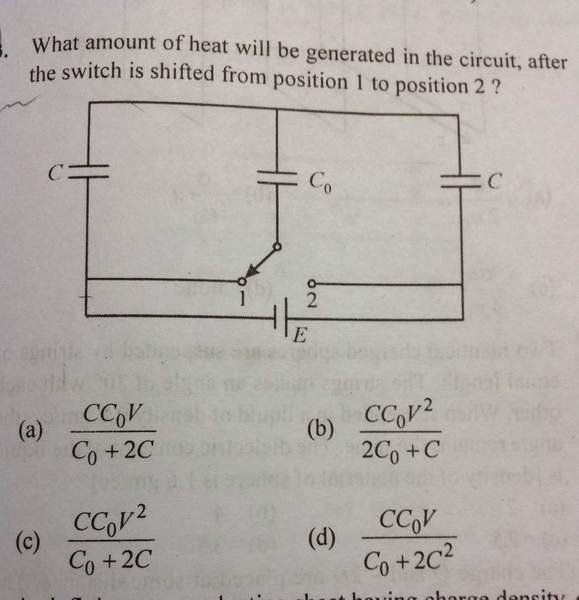
The discussion centers on the effects of switching polarity on capacitor energy and heat dissipation in a circuit involving capacitors C0 and C. When the switch is flipped, the energy dissipated as heat is equal to the energy delivered by the battery plus the energy stored in the capacitors before the switch is flipped, minus the energy stored after. The charge delivered by the battery is calculated as 2Q, where Q is derived from the relationship Q = CC0V/(2C + C0). The analysis concludes that the energy supplied by the battery results entirely in heat due to the lack of net energy added to the capacitors.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of capacitor charge and energy equations
- Familiarity with circuit analysis involving series and parallel components
- Knowledge of the relationship between voltage, charge, and energy (Q = CV)
- Basic principles of energy conservation in electrical circuits
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of energy dissipation in capacitors during switching events
- Learn about the impact of capacitor polarity on circuit behavior
- Explore advanced circuit analysis techniques for capacitors in series and parallel
- Investigate thermal effects in electrical components due to energy dissipation
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, physics students, and anyone involved in circuit design and analysis, particularly those focusing on capacitor behavior and energy management in electronic systems.