Discussion Overview
The discussion centers around the differences between two types of AC circuits, specifically a regular AC circuit and a live/hot & neutral AC circuit. Participants explore the implications of grounding on voltage levels and the nature of alternating current.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
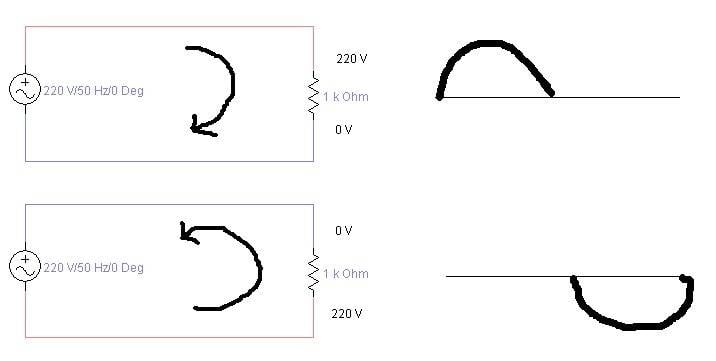
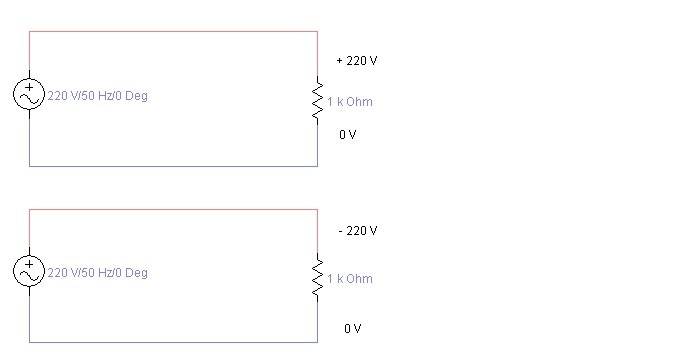
- Some participants question whether the two depicted circuits are fundamentally different, suggesting they may just be labeled differently.
- One participant emphasizes the importance of defining what is meant by "regular" AC circuit and the implications of grounding on voltage measurements.
- Another participant proposes two possible concepts of AC voltage behavior during half cycles, seeking clarification on which is correct.
- A participant explains that voltage is defined as the difference in potential between two points and discusses the dual purpose of grounding in circuits.
- There is a mention that grounding does not affect the circuit under normal conditions but is crucial for safety in case of faults.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the nature of the circuits and the role of grounding, indicating that multiple competing perspectives remain unresolved.
Contextual Notes
Some assumptions about the definitions of circuit types and grounding are not explicitly stated, leading to potential confusion in the discussion.