SUMMARY
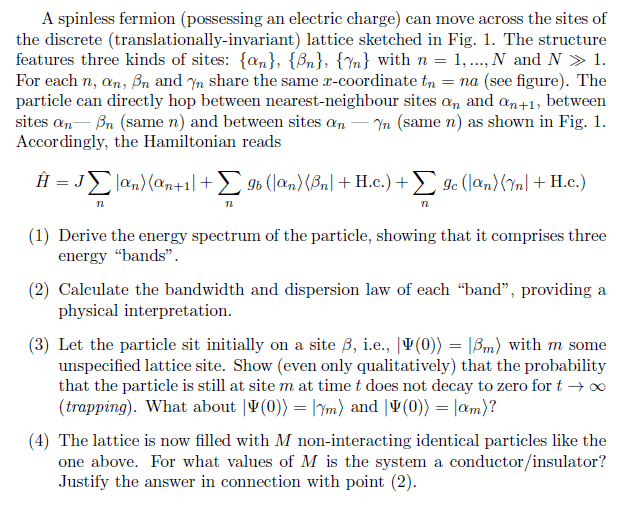
The discussion centers on the tight-binding model, where the energy spectrum of a particle is derived, resulting in three energy bands: E+(k), E−(k), and E0(k)=0. The derived dispersion laws reveal a flat energy band, prompting inquiries into its physical significance. The energy bands are mathematically expressed as E_{\pm}(k)=-Jcos(ka){\pm}\sqrt{J^2cos^2(ka)+g_c^2+g_b^2}. The implications of the particle's state as time approaches infinity are also explored.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of quantum mechanics principles
- Familiarity with the tight-binding model
- Knowledge of energy band theory
- Basic proficiency in mathematical expressions and dispersion relations
NEXT STEPS
- Research the physical significance of flat energy bands in condensed matter physics
- Explore the derivation of dispersion relations in the tight-binding model
- Study the implications of time evolution in quantum mechanics
- Investigate the effects of varying coupling constants (g_c and g_b) on energy bands
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, particularly those specializing in condensed matter physics, students studying quantum mechanics, and researchers interested in energy band structures and their implications.