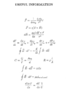SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on applying the Biot-Savart Law to calculate the magnetic field generated by a point charge. Participants clarify the integration bounds and the meaning of the infinitesimal length element, ##d\vec{s}##, emphasizing that it is not interchangeable with the total length of the wire. The correct integrand involves the cross product of ##d\vec{s}## and the vector ##\vec{r}##, which connects the wire to the point charge. The final magnetic field calculation requires integrating only the horizontal component of the magnetic field, ##dB_z##, which survives due to the geometry of the problem.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the Biot-Savart Law and its application in electromagnetism.
- Familiarity with vector calculus, particularly integration of vector fields.
- Knowledge of the right-hand rule for determining the direction of magnetic fields.
- Basic concepts of circular motion and geometry related to angles in three-dimensional space.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation and applications of the Biot-Savart Law in various configurations.
- Learn about vector calculus techniques, specifically focusing on cross products and their physical interpretations.
- Explore the concept of magnetic fields generated by different current configurations, such as loops and solenoids.
- Investigate the relationship between electric currents and magnetic fields, including Ampère's Law.
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics, particularly those studying electromagnetism, electrical engineering, or anyone involved in solving problems related to magnetic fields and forces on charged particles.