- #1
Ignitia
- 21
- 5
Homework Statement
The accompanying figure shows a current loop consisting of two concentric circular arcs and two perpendicular radial lines. Determine the magnetic field at point P.
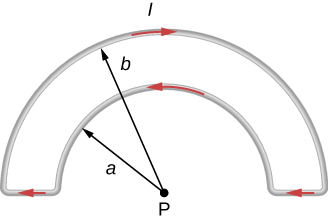
Homework Equations
B = μ/(4π) ∫ (I*dl x r)/r2
Btot = Ba - Bb
The Attempt at a Solution
For part a:
Ba = μ/(4π) ∫ (I*a*dθ)/a2
Ba = μI/(4πa) ∫dθ
Ba = μI/(4πa) * π
Ba = μI/(4a)
For part b:
Bb = μ/(4π) ∫ (I*b*dθ)/b2
Bb = μI/(4πb) ∫dθ
Bb = μI/(4πb) * π
Bb = μI/(4b)
So, for Btot = μI/(4a) - μI/(4b) which is only one half of the correct answer. What am I missing?
Bb = μI/(4πb) ∫dθ
Bb = μI/(4πb) * π
Bb = μI/(4b)
So, for Btot = μI/(4a) - μI/(4b) which is only one half of the correct answer. What am I missing?