You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
AI Thread Summary
To calculate the force required to lift a load 3 meters high, it's essential to consider the energy involved rather than just the force. The discussion highlights that the load is not attached to a lever arm, implying it must be thrown upwards. The key equation to use is the work-energy principle, which states that the work done by external forces equals the change in mechanical energy of the object. Specifically, the work done (W_F) is equal to the gravitational potential energy change (mgh), where m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height (3 meters). Additionally, the maximum distance (x) is influenced by the lever arm's length. Understanding these relationships allows for the calculation of the necessary force based on the energy required to achieve the desired height.
Physics news on Phys.org
Chen
- 976
- 1
Where is the picture?
kalpesh
- 6
- 0
I attached it in the thread
Dont know how to use it
Thanks
Kalpesh
Dont know how to use it
Thanks
Kalpesh
Chen
- 976
- 1
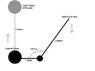
I can't see how you can lift the load 3 meters high when the lever connected to it is just 1 meter long. Or do you mean "throwing" the load 3 meters high, rather than lifting it while it's on the lever?
kalpesh
- 6
- 0
You got it right my friend
The ball / load is not attached to the arm.
Hence the ball needs to be thrown upwards.
The ball / load is not attached to the arm.
Hence the ball needs to be thrown upwards.
Michael D. Sewell
kalpesh,
You have given us a point of application, but no direction or sense.
-Mike
You have given us a point of application, but no direction or sense.
-Mike
kalpesh
- 6
- 0
Michal
I have changed the image for your ref.
please help me how to calculate the req. force whith the given angle and also if you change the angle.
Kalpesh
I have changed the image for your ref.
please help me how to calculate the req. force whith the given angle and also if you change the angle.
Kalpesh
turin
Homework Helper
- 2,314
- 3
You need to apply energy, not force (they are related, but it will be easier to first consider the required energy, and then translate that into how much force to apply).
kalpesh
- 6
- 0
Thanks TURIN
But in that case u will need to tell me how to find energy and then how to convert it to force.
Thanks
Kalpesh
But in that case u will need to tell me how to find energy and then how to convert it to force.
Thanks
Kalpesh
Chen
- 976
- 1
Generally speaking, the work done by all non-conservative forces is equal to the change in mechanical energy of the object. In your case:
{W_F}_{ext} = \Delta E_m = \Delta E_k + \Delta E_p
Since the inital velocity and final velocity are both zero, there is no change in kinetic energy so it comes down to this:
W_F = \vec F\cdot \vec x = mgh
{W_F}_{ext} = \Delta E_m = \Delta E_k + \Delta E_p
Since the inital velocity and final velocity are both zero, there is no change in kinetic energy so it comes down to this:
W_F = \vec F\cdot \vec x = mgh
turin
Homework Helper
- 2,314
- 3
And don't forget that the x vector has a maximum value (determined by the lever arm).
Similar threads
- Replies
- 9
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 12
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 9
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 10
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 5K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 7K
Hot Threads
-
I Explain Bernoulli at the molecular level?
- Started by user079622
- Replies: 251
- Classical Physics
-
B Simple mass/scale puzzle
- Started by DaveC426913
- Replies: 206
- Classical Physics
-
I How deep does it need to go for a physics theory to be consistent?
- Started by Aleberto69
- Replies: 50
- Classical Physics
-
I Solving a momentum problem where masses change after the collision
- Started by rdemyan
- Replies: 35
- Classical Physics
-
B Torque Calculation - Not a basic application
- Started by TeeBeeCee
- Replies: 37
- Classical Physics
Recent Insights
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 7
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 78
- General Math
-
Insights Why Vector Spaces Explain The World: A Historical Perspective
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 0
- General Math