- #1
MechEngJordan
- 17
- 0
Hello,
I'm currently working on a problem involving the calculation of an unknown voltage source of a circuit containing a resistor, inductor and load in series.
Unfortunately, the problem sheet does not give an answer at the end, so I am unsure as to whether my approach is correct -- hence this post. I suppose I'm really looking for guidance on how to tackle this kind of problem.
1. Homework Statement
Calculate the source voltage and draw the voltage and current phasor diagram for the single phase circuit.
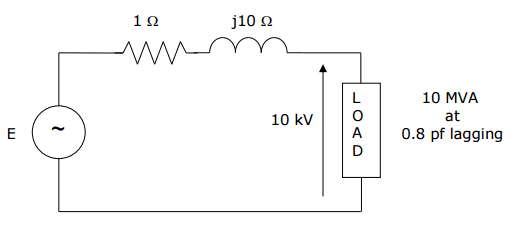
[tex]Real Power, P = \widetilde{|V|}\widetilde{|I|}cosφ[/tex]
[tex]Complex Power, S = \widetilde{V}\widetilde{I}^*[/tex]
[tex]Apparent Power, |S| = \widetilde{|V|}\widetilde{|I|}[/tex]
[tex]Power Factor, cosφ = \left(\frac{P}{|S|}\right)[/tex]
[/B]
I was undertaking the following approach:
From the load rating and power factor given, the apparent power and phase angle can be deduced; thus the power can be calculated from the power factor relationship.
The current may then be determined from the real power equation.
Now, voltage across each component can be calculated and the phasors summed to determine the source voltage.
Any input would be greatly appreciated. Thanks.
I'm currently working on a problem involving the calculation of an unknown voltage source of a circuit containing a resistor, inductor and load in series.
Unfortunately, the problem sheet does not give an answer at the end, so I am unsure as to whether my approach is correct -- hence this post. I suppose I'm really looking for guidance on how to tackle this kind of problem.
1. Homework Statement
Calculate the source voltage and draw the voltage and current phasor diagram for the single phase circuit.
Homework Equations
[tex]Real Power, P = \widetilde{|V|}\widetilde{|I|}cosφ[/tex]
[tex]Complex Power, S = \widetilde{V}\widetilde{I}^*[/tex]
[tex]Apparent Power, |S| = \widetilde{|V|}\widetilde{|I|}[/tex]
[tex]Power Factor, cosφ = \left(\frac{P}{|S|}\right)[/tex]
The Attempt at a Solution
[/B]
I was undertaking the following approach:
From the load rating and power factor given, the apparent power and phase angle can be deduced; thus the power can be calculated from the power factor relationship.
The current may then be determined from the real power equation.
Now, voltage across each component can be calculated and the phasors summed to determine the source voltage.
Any input would be greatly appreciated. Thanks.
Last edited: