Homework Help Overview
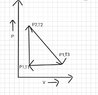
The discussion revolves around the concepts of heat transfer and internal energy changes in thermodynamics, particularly in the context of an ideal gas undergoing a full cycle. Participants are exploring the implications of different heat capacities and the relationship between work done and changes in internal energy.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are questioning whether the heat capacity should be Cp or Cv due to the nature of the process involving both pressure and volume changes. There is also a discussion about calculating work done and its relation to internal energy changes, with references to specific formulas and conventions.
Discussion Status
The discussion is active, with participants providing insights into the relationships between work, heat, and internal energy. Some guidance has been offered regarding the calculation of work and the implications of the ideal gas law, but no consensus has been reached on the specific heat capacity to use in this context.
Contextual Notes
Participants are navigating the complexities of a thermodynamic cycle, noting that the system returns to its initial state, which raises questions about the overall change in internal energy. There is an emphasis on ensuring that the signs of calculated values align with the chosen sign convention.