- #1
deathcloset
- 5
- 0
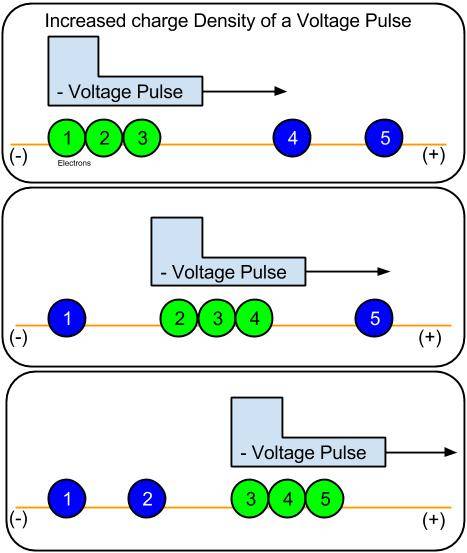
If I make a single, short (GHZ) negative voltage pulse propagate down a long, single wire which forms a closed circuit, will there be a corresponding negative charge density in the conductor (shown as bunched-up green electrons) which propagates with the pulse?