- #1
Constantinos
- 83
- 1
Hey!
Below you will find a piece of text I found on a paper. There are some things I don't get, perhaps you could help me.
What it means for the network to be lossless?
Also, why is the power flow equal to Re[Vi(t) Ii,k(t)*] and not outright Vi(t)*Ii,k(t) ? Why the complex conjugate?
I get the math, but not the definitions really!
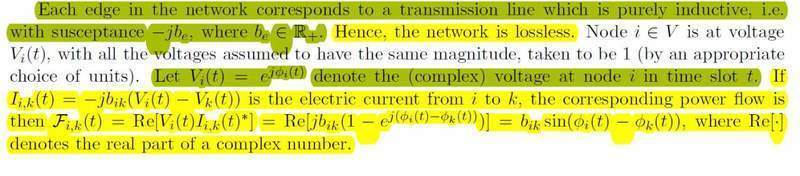
Below you will find a piece of text I found on a paper. There are some things I don't get, perhaps you could help me.
What it means for the network to be lossless?
Also, why is the power flow equal to Re[Vi(t) Ii,k(t)*] and not outright Vi(t)*Ii,k(t) ? Why the complex conjugate?
I get the math, but not the definitions really!