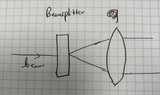
Collimation of a Gaussian beam
- Context: Graduate
- Thread starter Mubeen
- Start date
-
- Tags
- optics problem
Click For Summary
Discussion Overview
The discussion centers on the design of optics in Zemax for the collimation of a Gaussian beam, specifically focusing on off-axis rays. Participants explore the specifications of the incoming laser beam, the function of a beamsplitter, and the desired outcomes for beam collimation over a specified distance.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant seeks to design optics for collimating a Gaussian beam, clarifying that the incoming beam is a laser with a Gaussian intensity distribution.
- Another participant questions the specification of the incoming beam and the function of the beamsplitter, seeking clarification on whether it splits the beam into two equal intensity beams.
- A participant describes the beamsplitter as a diffractive optical element (DOE) that splits the beam at a 5-degree angle to the normal surface.
- Concerns are raised about the collimation of the beam, with one participant noting that laser beams are already collimated and asking how the participant intends to improve upon this.
- Participants discuss the Rayleigh range, with one providing specific parameters: a Rayleigh range of around 3 m, a wavelength of 1064 nm, and a beam waist radius of 1 mm.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying levels of understanding regarding the collimation process and the specifics of the beamsplitter. There is no consensus on the best approach to achieve the desired collimation, and multiple viewpoints on the effectiveness of the current setup remain unresolved.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the importance of the Rayleigh range and beam parameters in the discussion, indicating that these factors are crucial for determining the collimation effectiveness. However, the discussion does not resolve how these parameters interact with the proposed optical design.
Similar threads
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 16 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 6 ·
- · Replies 2 ·