- #1
TheRedDevil18
- 408
- 1
Here's the amplifier in question:
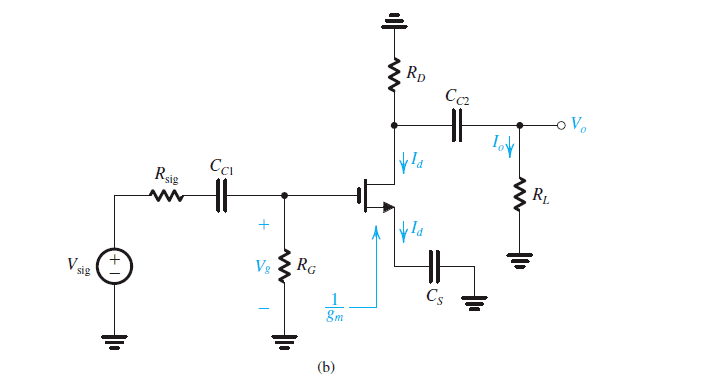
I'm not understanding this part:
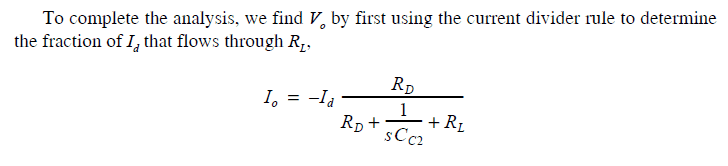
Why is Cs not included in the current divider ?
To my understanding of current divider, It = Id+Io, where It is the current flowing through Rd
So, Io = It*(1/Cs)/(1/Cc2)+RL
I'm not understanding this part:
Why is Cs not included in the current divider ?
To my understanding of current divider, It = Id+Io, where It is the current flowing through Rd
So, Io = It*(1/Cs)/(1/Cc2)+RL